On July 3, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service launched a plan to start out out killing 15,000 barred owls a yr throughout the Pacific Northwest, starting as shortly as this fall. This extraordinary initiative — better than a dozen years throughout the making — is supposed to save lots of a number of the imperiled northern observed owl from extinction.
Barred owls have been shifting west into observed owl territory for a few years, aggressively outcompeting them for prey and nesting web sites. If its plan is adopted, the federal firm will shortly launch what’s anticipated to be a three-decade advertising marketing campaign by which licensed hunters will in the end shoot virtually half a million barred owls.
“We’re wildlife conservation professionals, and we don’t take this flippantly,” acknowledged Bridget Moran, a space supervisor for the Fish and Wildlife Service in Bend, Oregon, who has been engaged on the method. “The observed owl is at a crossroads. Now we now have the science to level what we are going to do to protect observed owls, and [it’s] telling us that we must always deal with barred owls together with habitat to save lots of a number of them.”
The plan, as supplied in a closing environmental impression assertion, has garnered opposition, largely from animal welfare and anti-hunting groups, however as well as assist from mainstream environmental groups.
The Fish and Wildlife Service adopted its plan based largely on a look at of “invader elimination,” revealed in 2021, by which researchers organize 5 pairs of examine plots. On one plot, they left barred owls and observed owls to their very personal devices. On the alternative plot, they shot any barred owls that entered.
An extended-term space experiment confirmed that the place barred owls have been killed, the inhabitants of observed owls stabilized.
The researchers eradicated 2,485 barred owls over numerous years throughout the managed plots. The place barred owls and observed owls have been left alone, the inhabitants of the threatened species declined spherical 12 p.c yearly. The place barred owls have been killed, the inhabitants of observed owls stabilized.
“Utilizing long-term space experiments to examine the effectiveness of removals in benefitting impacted native species is unusual,” acknowledged David Wiens, a U.S. Geological Survey biologist and the lead creator of the paper. “This look at is the largest space experiment ever carried out on the demographic penalties of invasive opponents between predatory birds.”
Steep inhabitants declines of northern observed owls, which reside solely in old-growth and mature second-growth forests of the Pacific Northwest, raised alarms better than 35 years prior to now. Continued logging of those forests, specialists acknowledged on the time, would drive the hen to extinction. In June 1990, the hen was listed as a threatened species throughout the Pacific Northwest and logging in its habitat was restricted.
The federal movement created a storm of controversy, nonetheless it prevented the extinction of the observed owl. Efforts to cease the disappearance of the owl, then and now, mustn’t almost defending a charismatic predator. Seen owls are an indicator species for the properly being of the old-growth ecosystem: If a forest has ample populations of flying squirrels, mice, and salamanders to keep up observed owls, the forest is extra more likely to be varied and healthful. Seen owls solely reside in mature forests, whereas barred owls can thrive in every youthful and outdated forests and eat a far wider range of prey.

Left: a barred owl. Correct: a observed owl.
Ray Bosch / U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service; David Roelofs / Bureau of Land Administration
Logging of outdated improvement forest on public lands has, for basically essentially the most half, halted, and some logged areas in the intervening time are being restored. Nonetheless whereas the logging battles have died down, the model new controversy over the suitable response to what has been referred to as an invasion of barred owls has heated up as a result of the Fish and Wildlife Service’s closing selection nears.
Biologists think about that the barred owl began shifting out of jap North America and all through Canada with the westward movement of European settlers. In a two-part paper, the earlier FWS biologist Kent Livezey concluded that the scarcity of bushes on the Good Plains created a barrier to owl movement until settlers appeared. They excluded hearth from ecosystems, which in the end allowed forests to unfold, and they also planted bushes on farms and in cities, all of which equipped an enlargement of roosting habitat. Wheat and totally different grain farms might need elevated the numbers of mice and totally different prey.
Barred owls have been first observed in Washington, Oregon, and California throughout the Seventies, and instantly there are better than 100,000 of them residing throughout the northern observed owl’s territory in these states, primarily based on federal biologists.
When barred owls switch into observed owl habitat, the impression is speedy and thorough. The interlopers are greater and additional aggressively territorial. They drive observed owls away from their nests and outcompete the smaller birds for meals. A minimum of half the observed owls throughout the forests of the West have been misplaced to barred owls, says the Fish and Wildlife Service, and some areas have misplaced three-quarters of their historic inhabitants. When barred owls colonized Redwoods State and Nationwide Parks in Northern California, starting in 1987, the observed owls all nonetheless disappeared.
Biologists considered capturing and sterilizing barred owls, nonetheless they may nonetheless return to their territory and displace observed owls.
The plan to shoot barred owls will defend the northern observed owl, a subspecies that occurs in Northern California, Oregon, Washington, and southern British Columbia, which now has fewer than 5 northern observed owls, along with a lone female.
The number of northern observed owls within the USA isn’t precisely recognized: Estimates put the inhabitants at only some thousand. Its persevering with decline, nonetheless, is steep. In areas the place roughly 200 observed owls lived throughout the early 2000s, solely two or three birds keep, acknowledged Robin Bown, a FWS biologist in Oregon. The hen is presently listed as threatened. FWS scientists say it is warranted for itemizing as endangered, nonetheless the corporate says such movement is precluded on account of it ought to consider better priority species.
The California observed owl, one different subspecies, was ultimate yr proposed for itemizing as endangered throughout the southern part of its range and threatened throughout the Sierra Nevada. Barred owls are merely beginning their invasion of that hen’s habitat, and the FWS method is to dispatch them as shortly as they’re detected. The Mexican observed owl is listed as threatened in every the U.S. and Mexico nonetheless simply is not presently threatened by the barred owl.
Though the plan to kill a complete lot of a whole lot of owls is extreme, federal wildlife officers say totally different decisions merely aren’t accessible. Capturing the birds and shifting them elsewhere was contemplated. “We contacted the jap states the place barred owls are native, to see within the occasion that they wished barred owls once more,” acknowledged Bown. “They acknowledged ‘no.’ Their present habitat is already full.” Transferring them may also unfold sickness and parasites. Moreover they considered capturing and caging barred owls, nonetheless sustaining so many birds might be prohibitively pricey, certainly not ideas the reality that there aren’t adequate licensed companies to accommodate barred owls for the rest of their lives.
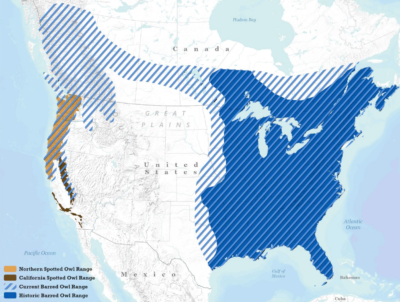
The ranges of barred owls, northern observed owls, and California observed owls.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Biologists moreover considered “reproductive interference” — capturing barred owls and sterilizing them. Nonetheless launched owls would merely return to their territory, displacing observed owls, and preserve there until they died, Bown acknowledged.
The federal authorities has prolonged experience with eliminating wild animals to guard endangered species. To protect endangered warblers and totally different songbirds, a complete lot of a whole lot of cowbirds, a nest parasite, have been killed yearly. Wildlife managers in Washington and Oregon lethally inject sea lions to protect salmon runs. Feral hogs are routinely slaughtered to protect threatened and endangered species.
The Fish and Wildlife Service plans to work with explicit individual landowners and representatives from tribes and federal and state companies, teaching and certifying volunteers to remove the invasive species as humanely as doable. The service emphasizes that there isn’t any such factor as a public looking out of barred owls permitted.
“Sooner than anyone can try this, they’ve to meet our {{qualifications}} [for permitting],” acknowledged Bown. “They should have teaching, info, and experience.” Shooters would possibly wish to know their owls. Barred owls have a specific identify that seems like “Who cooks for you?” Though observed and barred owls are equally colored, barred owls are a bit greater and have vertical and horizontal striping, whereas observed owl markings are horizontal.
Animal rights groups identify the movement of invasive owls ‘adaptive range enlargement’ and an instinctive response to native climate change.
“Now we now have eradicated 4,500 barred owls with the similar protocol in experimental removals throughout the ultimate 12 or 15 years with no single non-target harm or dying,” acknowledged Bown. Shooters will head into the woods at night time time, with flashlights and megaphones. “We’ll enterprise territorial barred-owl sounds,” acknowledged Bown, explaining what’s known as a callback survey. “If barred owls are there, they might reply and usually technique us.” Shooters must be inside 100 toes of their aim, she acknowledged, and “have an excellent clear shot.” Carcasses will shortly be buried throughout the forest.
Spherical 15,000 barred owls will seemingly be killed yearly for 30 years — totaling some 450,000 birds. Biologists estimate the utmost number of owls eradicated yearly will seemingly be decrease than the estimated annual improvement of the entire barred owl inhabitants.
The barred owl elimination plan has drawn criticism along with reluctant assist. Hilary Franz, the Commissioner of Public Lands for Washington State, has concerns regarding the culling. She posted suggestions, which she despatched to Secretary of the Inside Deb Haaland, regarding the deliberate culling on YouTube. “It raises monumental portions of questions,” she acknowledged. “How can the Fish and Wildlife Service guarantee that solely barred owls will seemingly be centered? How can we forestall the surviving barred owls from merely recolonizing and repopulating the very areas we try to guard? And with so many species now coping with extinction, how can we justify spending virtually a billion {{dollars}} on one species when our funding and sources are restricted?”
The Fish and Wildlife Service has acknowledged the worth of the enterprise has not however been tabulated.

Wildlife technician Jordan Hazan info data from a barred owl killed as part of an experiment geared towards preserving observed owls, Corvallis, Oregon, October 2018.
Ted S. Warren / AP {Photograph}
The primary opposition has come from animal rights and welfare organizations. In March, 75 organizations led by Animal Wellness Movement president Wayne Pacelle despatched a letter to Haaland opposing the capturing of the birds, calling the movement of invasive owls “adaptive range enlargement” and an instinctive response to native climate change. “We will not victimize animals for adapting to human perturbations of the setting, possibly significantly the all-encompassing outcomes of native climate change,” they wrote.
The Center for Natural Vary, within the meantime, is supportive of the cull. “I hate to see any animal killed, nonetheless the observed owl will certainly go extinct with out an effort to chop again invasive barred owl populations,” acknowledged Noah Greenwald, the conservation group’s endangered species director. “I’m hopeful that along with protections for old-growth forests on federal lands, barred owl administration will give the observed owl an precise chance at survival.” The American Rooster Conservancy moreover helps the plan, as do some, nonetheless not all, Audubon chapters.
Denver Holt, a primary owl researcher who’s president of the Owl Evaluation Institute, in Charlo, Montana, questions whether or not or not the birds are actually invasive and believes their range enlargement all through the boreal forest in Canada is also pure. “I’m concerned,” he acknowledged. “They’re using the invasive class to kill so many owls. I’d desire to see an neutral analysis.”
Nonetheless the Fish and Wildlife Service says movement must be taken now. “If we don’t try this, the observed owl will go extinct,” acknowledged Bown. “That’s not a troublesome prediction to make.”
Correction, July 23, 2024: An earlier mannequin of this textual content incorrectly stated that wildlife managers in Washington and Oregon lethally inject sea otters to protect salmon runs. They inject sea lions, not sea otters.
